Simple steps to troubleshoot network issues:
1. Identify the Problem
→ Understand the nature of the issue (internet access, slow speed, DNS errors, etc.). Check if the problem is with one device or across multiple systems.
2. Use ipconfig (Windows)
→ Open Command Prompt and type ipconfig.
- IP Address: Check if it starts with
169.x.x.x. If so, the system is not receiving a valid IP from the router. - Default Gateway: This is your router’s IP address.
- Try:
ipconfig /releaseipconfig /renew
This refreshes the IP address and can often solve DHCP-related issues.
- If issues persist, plug the computer directly into the modem via Ethernet. If it works, the router is likely at fault.
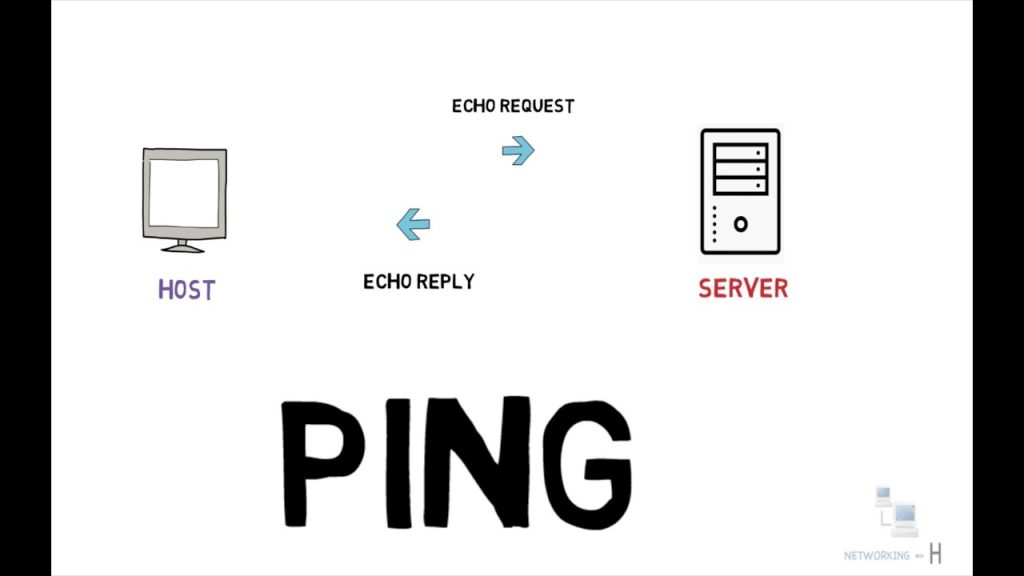
3. Use Ping and Tracert
→ Test connectivity and trace the data path:
- Ping Google DNS:
ping 8.8.8.8
Add-tto keep pinging:ping 8.8.8.8 -t - Tracert:
tracert 8.8.8.8
This shows each “hop” between your device and the destination. If it fails early, the issue may be in your local network.
4. Perform a DNS Check
→ Use nslookup to verify domain name resolution:
- Example:
nslookup google.com - If errors like “Server Failure”, “Refused”, or “Network Unreachable” appear, there may be an issue with your DNS server or the destination server.
5. Check Physical Connections
→ Ensure all Ethernet and power cables are properly connected and LED lights are active. Try a different cable or port if necessary.
6. Restart Networking Devices
→ Reboot your router, modem, and affected computer. This clears temporary errors and reinitializes the network stack.
7. Check Firewall and Security Software
→ Ensure that firewalls or antivirus programs are not blocking internet access or specific apps. Try temporarily disabling them for testing.
8. Disable/Enable Network Adapter
→ On your computer, disable and then re-enable the network adapter to reset its connection state.
9. Check for IP Conflicts
→ Ensure that no other device is using the same IP address. Assign static IPs or use DHCP correctly.
10. Review Database Logs (if applicable)
→ If network-connected applications are slow or not responding, check if the database is overloaded, misconfigured, or experiencing errors.
11. Check Virus and Malware Protection
→ Malware can interfere with networking. Make sure your antivirus is running and scan the system for infections.
12. Contact ISP
→ If all local troubleshooting fails, contact your Internet Service Provider. Use your mobile device to check for local outages or issues in your area.